 设计模式-抽象工厂模式
设计模式-抽象工厂模式
# 设计模式-抽象工厂模式
在工厂模式中 每一个具体工厂只需要生产一种具体产品,但是在抽象工厂模式中一个具体工厂可以生产一组相关的具体产品。、
这样的一组产品成为产品族,产品族中的每一个产品都分属于某一个产品等级结构。
- 产品族:由同一个工厂生产的位于不同产品等级结构中的一组产品。比如运动产品工厂生产的篮球鞋、跑步鞋、短袖。
- 产品等级结构:产品的继承关系。运动鞋可以分为篮球鞋、跑步鞋,篮球鞋又可以分为低帮、高帮。

适用场景:
系统中有多于一个的产品族,而每次只使用其中某一个产品族。
优点:
当一个产品族中的多个对象被设计成一起工作时,它能保证客户端始终只使用同一个产品族中的对象。
缺点:
产品族扩展非常困难,要增加一个系列的某一产品,既要在抽象的 Creator 里加代码,又要在具体的里面加代码。
# 案例
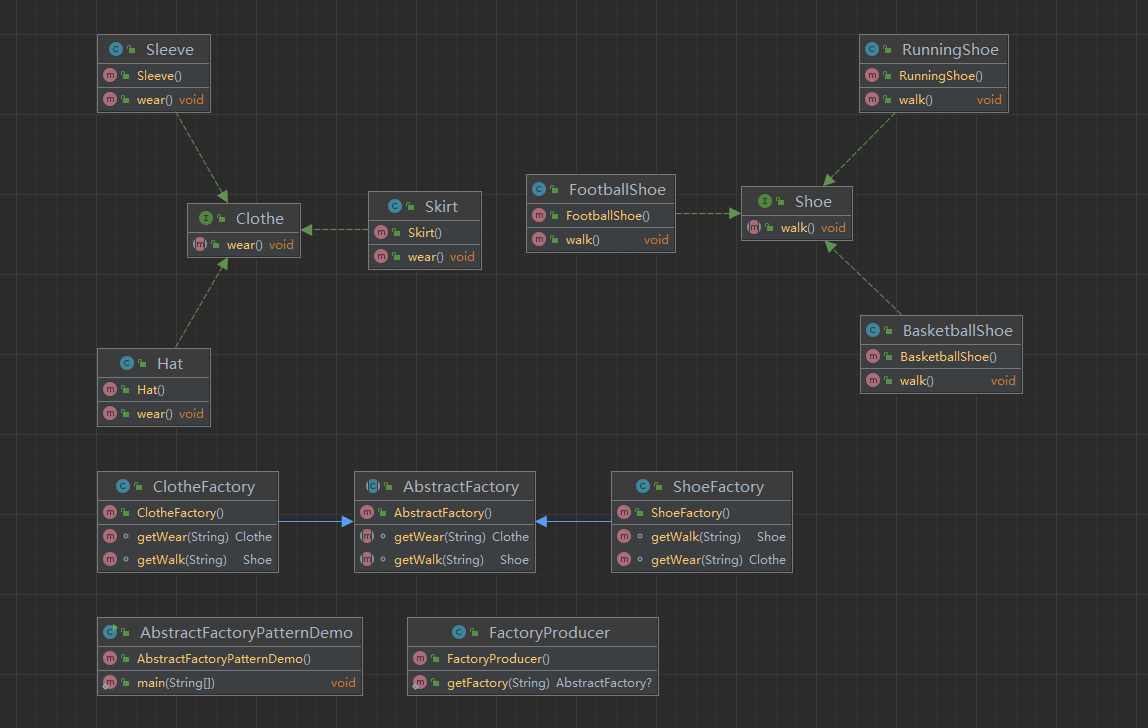
衣服接口:
public interface Clothe {
/**
* 穿衣服
*/
void wear();
}
衣服:
public class Skirt implements Clothe{
@Override
public void wear() {
System.out.println("穿裙子");
}
}
public class Hat implements Clothe{
@Override
public void wear() {
System.out.println("穿帽子");
}
}
public class Sleeve implements Clothe{
@Override
public void wear() {
System.out.println("穿长袖");
}
}
鞋子接口:
public interface Shoe {
/**
* 走路
*/
void walk();
}
鞋子:
public class BasketballShoe implements Shoe{
@Override
public void walk() {
System.out.println("篮球鞋走路");
}
}
public class FootballShoe implements Shoe{
@Override
public void walk() {
System.out.println("足球鞋走路");
}
}
public class RunningShoe implements Shoe{
@Override
public void walk() {
System.out.println("跑步鞋走路");
}
}
抽象工厂:
public abstract class AbstractFactory {
/**
* 获取走路方法
* @param shoeType 鞋子种类
* @return
*/
abstract Shoe getWalk(String shoeType);
/**
* 获取穿戴方法
* @param clotheType 衣服种类
* @return
*/
abstract Clothe getWear(String clotheType);
}
衣服工厂:
public class ClotheFactory extends AbstractFactory {
@Override
Shoe getWalk(String shoeType) {
return null;
}
@Override
Clothe getWear(String clotheType) {
if (clotheType == null) {
return null;
}
if ("Sleeve".equalsIgnoreCase(clotheType)) {
return new Sleeve();
} else if ("Hat".equalsIgnoreCase(clotheType)) {
return new Hat();
} else if ("Skirt".equalsIgnoreCase(clotheType)) {
return new Skirt();
}
return null;
}
}
鞋子工厂:
public class ShoeFactory extends AbstractFactory{
@Override
Shoe getWalk(String shoeType) {
if (shoeType == null) {
return null;
}
if ("BasketballShoe".equalsIgnoreCase(shoeType)) {
return new BasketballShoe();
} else if ("FootballShoe".equalsIgnoreCase(shoeType)) {
return new FootballShoe();
} else if ("RunningShoe".equalsIgnoreCase(shoeType)) {
return new RunningShoe();
}
return null;
}
@Override
Clothe getWear(String clotheType) {
return null;
}
}
工厂生产者:
public class FactoryProducer {
public static AbstractFactory getFactory(String choice){
if("Shoe".equalsIgnoreCase(choice)){
return new ShoeFactory();
} else if("Clothe".equalsIgnoreCase(choice)){
return new ClotheFactory();
}
return null;
}
}
实现:
public class AbstractFactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建衣服工厂
AbstractFactory clotheFactory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("Clothe");
// 衣服工厂创建衣服
Clothe hat = clotheFactory.getWear("Hat");
Clothe sleeve = clotheFactory.getWear("Sleeve");
Clothe skirt = clotheFactory.getWear("Skirt");
hat.wear();
sleeve.wear();
skirt.wear();
// 创建鞋子工厂
AbstractFactory shoeFactory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("Shoe");
// 鞋子工厂创建鞋子
Shoe basketBall = shoeFactory.getWalk("BasketballShoe");
Shoe running = shoeFactory.getWalk("RunningShoe");
Shoe football = shoeFactory.getWalk("FootballShoe");
basketBall.walk();
running.walk();
football.walk();
}
}
# 参考
上次更新: 2024/06/29, 15:13:44
