 Pytorch
Pytorch
# 一、分类和回归
- 分类是预测一个离散标签的任务(硬币的正反)
- 回归是预测一个连续数量的任务(股价的走势)
# 二、张量创建
一个张量是一个数字、向量、矩阵或任何n维数组
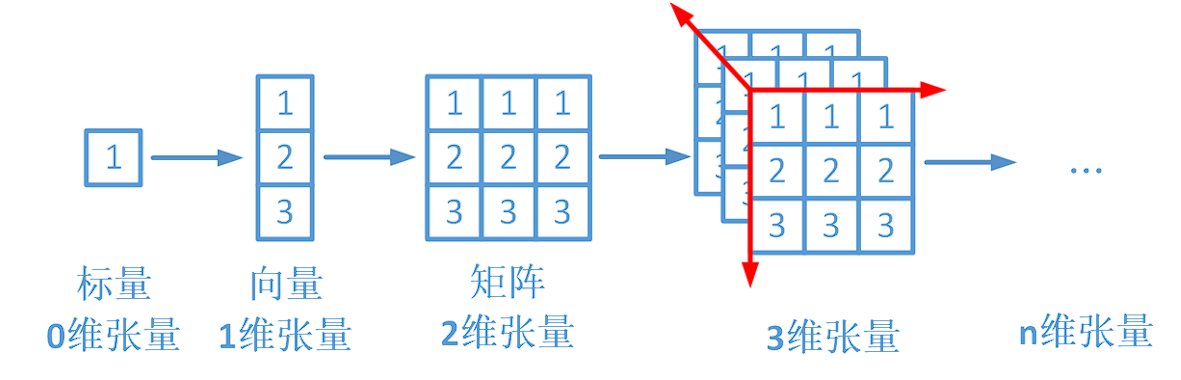
# 1、直接创建
torch.tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False)
- data: 数据,可以是list,numpy
- dtype: 数据类型,默认与data的一致
- device: 所在设备,cuda/cpu
- requires_grad: 是否需要梯度
- pin_memory: 是否存于锁页内存
a = torch.tensor([[0.1, 1.2], [2.2, 3.1], [4.9, 5.2]])
print(a)
# 2、按照数值创建
torch.zeros(*size, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
- size: 张量的形状,如(3, 3)、(3, 224, 224)
- out: 输出的张量
- layout: 内存中布局形式,有strided, sparse_coo等
- device: 所在设备,gpu/cpu
- requires_grad: 是否需要梯度
torch.zeros(2, 3)
类似的方法:
- torch.zeros_like
- torch.ones
- torch.ones_like
# 三、张量操作
# 1、基本操作
将张量按维度dim进行拼接
torch.cat(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
import torch
a = torch.randn(2,3)
print(a)
b = torch.cat((a, a, a), 1)
print(b)
tensor([[-0.4353, -1.5063, -2.1222],
[-2.3913, -1.3487, 0.2826]])
tensor([[-0.4353, -1.5063, -2.1222, -0.4353, -1.5063, -2.1222, -0.4353, -1.5063,
-2.1222],
[-2.3913, -1.3487, 0.2826, -2.3913, -1.3487, 0.2826, -2.3913, -1.3487,
0.2826]])
在新创建的维度dim上进行拼接
torch.stack(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
将张量按维度dim进行平均切分
torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim=0)
将张量按维度dim进行切分
torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
# 2、张量变化
变换张量形状
torch.reshape(input, shape)
import torch
a = torch.arange(4.)
print(a)
b = torch.reshape(a, (2, 2))
print(b)
tensor([0., 1., 2., 3.])
tensor([[0., 1.],
[2., 3.]])
交换张量的两个维度
torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1)
- input:要交换的张量
- dim0:要交换的维度
- dim1:要交换的维度
import torch
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(x)
b = torch.transpose(x, 0, 1)
print(b)
tensor([[-0.1400, 0.1028, -0.6031],
[-0.1887, -0.1407, 1.5659]])
tensor([[-0.1400, -0.1887],
[ 0.1028, -0.1407],
[-0.6031, 1.5659]])
2维张量专置
x = torch.randn(())
torch.t(x)
上次更新: 2024/06/29, 15:13:44
